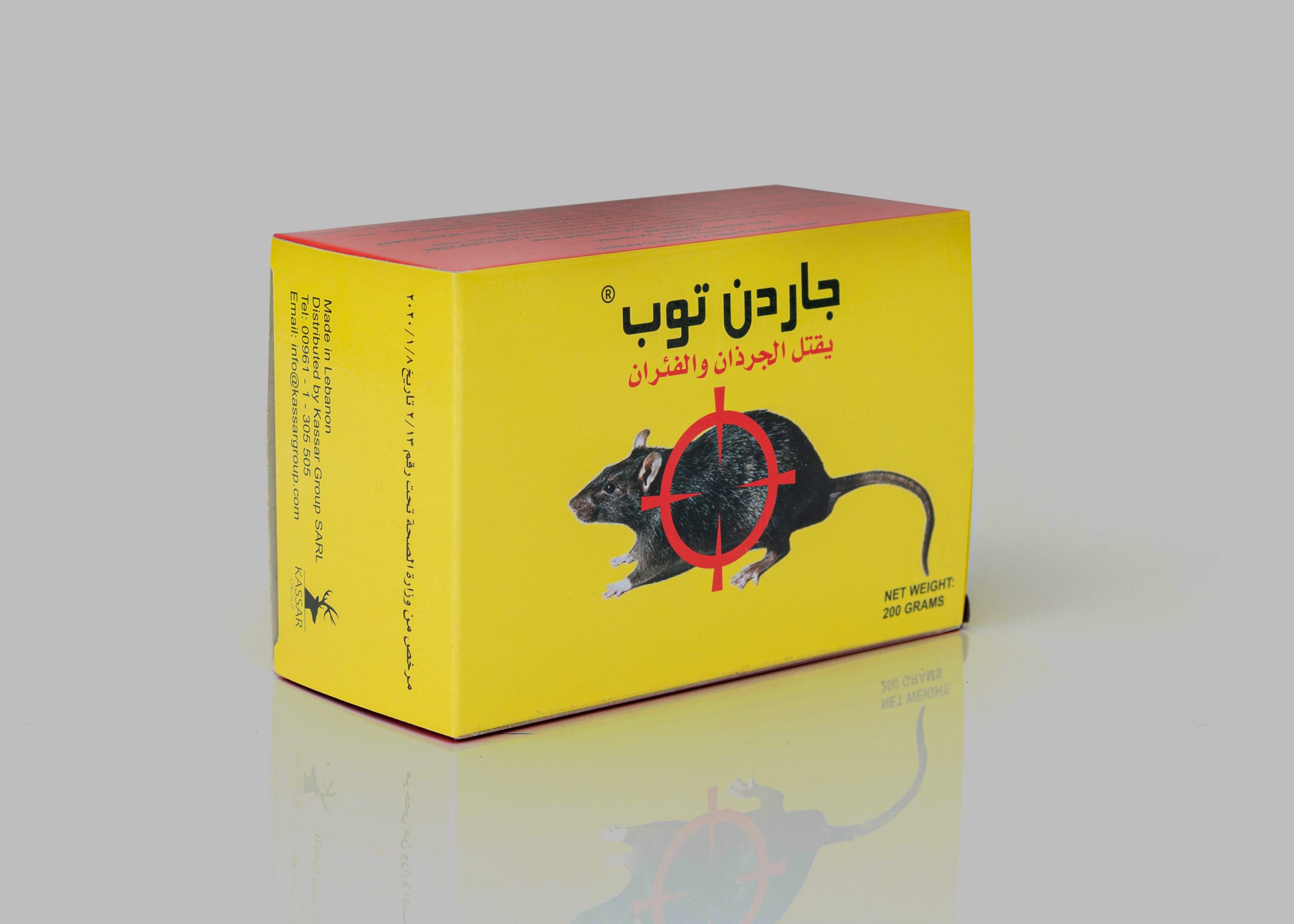
Why Does the World Still Buy Pesticides?
The use of pesticides is under criticism due to pressure from environmental and sustainability activists (individuals and social businesses) worldwide.
The public health problem created by pests worldwide still needs to be resolved by the present methods, despite the trend toward using alternatives such as organic insecticides or repellents.
When you buy pesticides, you are using a long-term solution because pesticides attempt to manage a variety of pests and disease carriers, such as mosquitoes, ticks, rats, and mice. For instance, weeds, insect infestations, and illnesses are all controlled through insecticides in agriculture.
There are several pesticides you can buy, as they come in various forms, each designed to be efficient against a particular insect. Several instances include:
- Buying Algaecides prevents algae from growing or killing it.
- Buying Antimicrobials regulates bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms.
- Mold, mildew, and rust are all fungal problems that fungicides
- Buying Herbicides eradicates undesirable plants, generally known as weeds, and/or prevents their growth.
- Buying Disinfectants keeps bacteria, viruses, and other organisms under control.
- Flying and crawling insects are controlled when you buy insecticides.
- Buying Insect Growth Regulators prevent insects from growing and reproducing normally.
- Rats and mice are killed when you buy rodenticides.
If everybody follows the instruction, we are safe.
Generally, the Ministry of Environment, Agriculture, or Health has primary authority for registering, approving, monitoring compliance, and enforcing pesticide use. The overall intent of the label is to provide clear directions for effective pesticide performance while reducing risks to human health and the environment.
The authorities analyze the pesticide registration process’s scientific, legal, and administrative aspects.
The pesticide’s components, the specific location or crop where it will be applied, the quantity, frequency, and timing of application, as well as the methods for storage and disposal.
They examine a wide range of potential negative impacts on human health and the environment related to the usage of the product while reviewing a pesticide registration application. The company that wants to manufacture the pesticide must provide data from studies that adhere to our testing requirements.
They create risk evaluations that examine the possibility of harm to non-target organisms and endangered species and people, animals, fish, and plants. Also, the potential contamination of groundwater or surface water due to spray drift, runoff, and leaching.